

CSS syntax consists of a set of rules that define how elements on the web page should be styled.
Watch the following video introduction to CSS syntax from the w3schools YouTube channel:
A CSS rule has two main parts:
{}.Each declaration consists of a property and a value, separated by a colon :. Declarations are ended with a semicolon ;.
Here's the basic structure of a CSS rule:
selector {
property: value;
property: value;
}
h1 {
color: blue;
font-size: 24px;
}
h1 (selects all Heading 1 <h1> elements in the document)color: blue; (sets the text color to blue)font-size: 24px; (sets the font size to 24 pixels)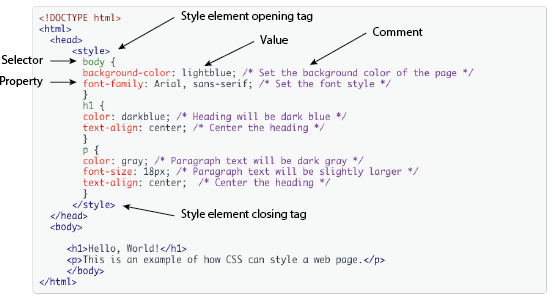
Selectors are like labels that tell your web page which parts to change with a certain style. For example, if you want to change the color of all headings, you use a selector to indicate that those heading elements should get the new color. There are different types of selectors, which will be covered in the next section.
For now, the only one you should remember is this one:
Universal Selector: Targets all elements in the document.
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
Removes margin and padding from all elements.
CSS provides many properties to style elements, such as:
p {
color: black;
background-color: lightgray;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
This rule styles all <p> (paragraph) elements with:
You can add comments in CSS to explain your code. Comments are ignored by the browser. Use /* to start a comment and */ to close it.
/* This is a comment */
h1 {
color: blue; /* This is another comment */
}
CSS stands for "Cascading Style Sheets," which means that styles can cascade, or fall in order, from parent to child elements. Styles applied to a parent element can affect child elements unless otherwise overridden.
color and font-size) are inherited by child elements, while others (like margin and padding) are not.
CSS syntax is a combination of selectors and declarations. The selector tells which element to style, and the declaration tells how to style it using properties and values. As you learn more CSS, you’ll become more comfortable working with different types of selectors, properties, and the cascade to build beautiful web designs.